FOMC RATE DECISION KEY POINTS:
- Federal Reserve raises its benchmark rate by 75 basis points to 3.00%-3.25%, in line with market expectations
- Policymakers downgrade their GDP estimates, while revising upwards the inflation outlook
- The September dot-plot signals a more hawkish tightening path than envisioned in the June Summary of Economic Projections
Trade Smarter - Sign up for the DailyFX Newsletter
Receive timely and compelling market commentary from the DailyFX team
Subscribe to Newsletter
Most Read: Growth Versus Value Stocks - How Interest Rates Affect Valuations
MARKET REACTION
Second Update at 3:20 pm ET
The Fed’s chair retained a forceful tone during his press conference, indicating that the FOMC seeks to return to a “sufficiently restrictive” stance to restore price stability, but pointed out that the committee is split between 100 and 125 basis points of additional tightening for the rest of this year.
He also repeated that the historical record cautions against prematurely loosening policy, but that warning was offset by comments indicating that at some time “it may become appropriate” to slow the pace of interest rate increases, an observation that appeared to have eased some of Wall Street’s worst fears.
Despite the hawkish message, risk assets managed to mount a recovery, with the S&P 500, Nasdaq 100 and Bitcoin all moving higher in late trading. Gold prices also rallied, jumping as much as 1.2% after the press event. Meanwhile, the U.S. dollar trimmed some gains as U.S. Treasury yields started to retrace their initial advance.
Looking ahead, once markets reassess today’s events and realize the monetary policy environment will become increasingly hostile to the economy and speculative appetite, risk assets may resume their decline. That said, it wouldn’t be surprising if markets reverted lower in the coming days, as traders reload their short positions.
Updated at 2:25 pm ET
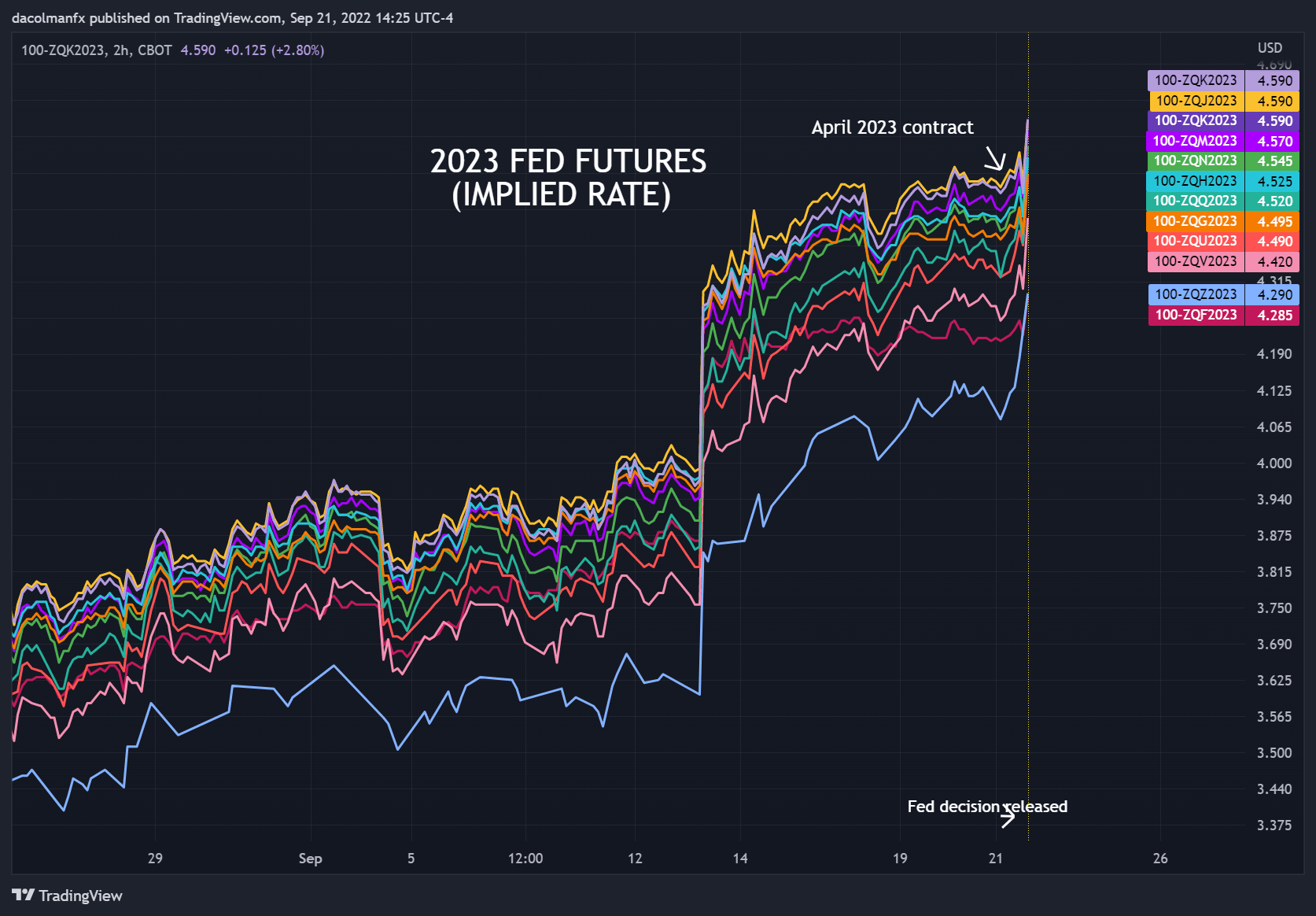
Prior to the central bank's announcement, Fed funds futures were signaling a terminal rate of around 4.5% during the second quarter of next year, but market expectations quickly adjusted higher to match the Fed's more aggressive estimates reflected in the updated dot plot, which pointed to 4.6% as a final destination for borrowing costs in 2023 while simultaneously ruling out premature cuts.
The reassessment of the monetary policy outlook pushed U.S. Treasury yields higher across the curve, with the 2-year note rising above the 4.07% threshold for the first time since 2007. Bond moves bolstered the U.S. dollar, driving the DXY index to its best levels in more than two decades. On the other hand, interest rate-sensitive precious metals reacted negatively, driving gold to trim most session's gains.
Meanwhile, risk assets took a sharp turn to the downside, with the S&P 500 and Nasdaq 100 falling more than 0.5%. Bitcoin also slumped to trade flat, erasing a 3% advance, as traders rushed to trim speculative positions that could suffer in less accommodative environments.
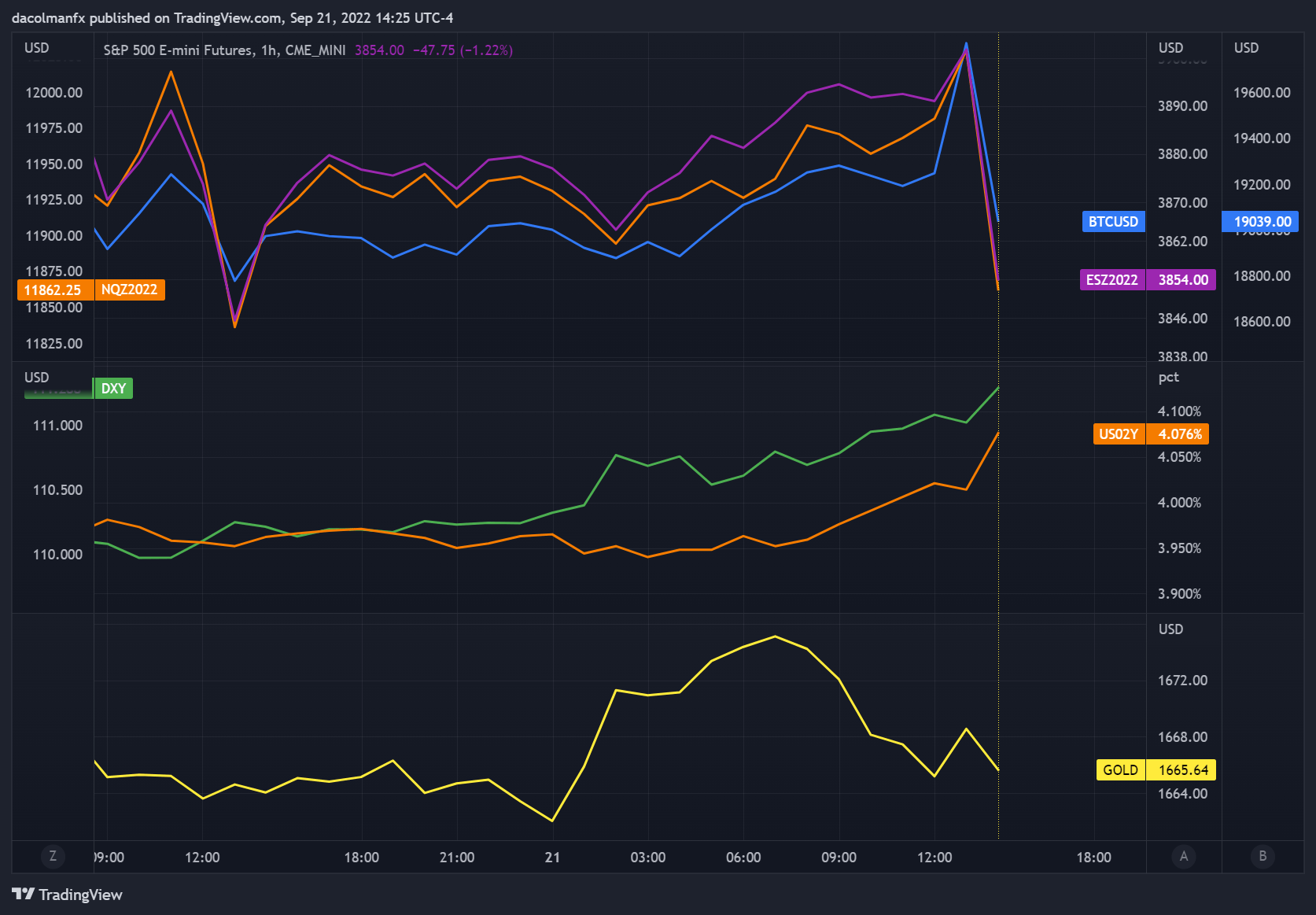
Source: TradingView
Original Post 2:10 pm ET
After two days of intense deliberations, the Federal Reserve concluded its September meeting this afternoon. The FOMC took another aggressive step in the fight to restore price stability and opted to raise its benchmark rate by three-quarters of a percentage point to 3.00-3.25%, in line with consensus expectations. This decision, which takes the federal funds rate well past the “neutral level” and into restrictive territory was reached by unanimous vote.
The U.S. central bank has been removing accommodation at the fastest pace since the early 1980s, delivering a total of 300 basis points of tightening since the start of the cycle in March, with a clear and unwavering goal in mind: to rein in rampant inflation. The Fed wants to achieve this part of its mandate by slowing the economy via tighter financial conditions in the form of higher mortgage, credit card and loan rates as well as lower stock prices. Together, these variables tend to negatively affect spending, business investment and hiring plans, leading to weaker aggregate demand. Over time, this combination of factors helps moderate inflationary pressures, although the lag is often unpredictable.
While annual CPI eased to 8.3% in August from 8.5% in July, it remained more than 4 times above the Fed’s 2% long-term target. What’s more, the core gauge advanced more than anticipated, clocking in at 6.3% from 5.9% previously amid accelerating rental costs, a sign that the price outlook remains extremely uncertain and biased to the upside.
The Fed’s front-loaded hiking regime has been responsible for the sharp rally in the U.S. dollar this year that pushed the DXY index to multi-decade highs earlier this month. The normalization process has also catalyzed a major sell-off in risk assets, from equities to cryptocurrencies, as investors have rushed to trim speculative positions amid shrinking liquidity. With the era of easy money ending, volatility is likely to remain elevated, keeping market sentiment on edge and preventing risky assets from making a lasting recovery. This means that the S&P 500 and Bitcoin are not out of the woods yet.
Related: Central Banks and Monetary Policy - How the Fed Controls Inflation
Recommended by Diego Colman
Get Your Free Equities Forecast
FOMC POLICY STATEMENT
The statement offered a downbeat message on economic activity, noting that spending and production indicators are showing modest growth.
On the labor market, the document stressed that the unemployment remains low, acknowledging that job gains remain strong, providing a vote of confidence in the outlook.
The central bank reiterated that inflation is high, reflecting supply and demand imbalances related to the coronavirus health crisis, rising food and energy costs, and broader price pressures. In addition, the bank said it continues to be attentive to inflation risks.
On monetary policy, the FOMC maintained the same forward guidance as previous statements, indicating that ongoing increases in the target range will be appropriate, signaling policymakers are not yet done with aggressive hikes.
Stay tuned for market analysis of today’s decision and Chairman Powell's press conference
Related: The Federal Reserve Bank - A Forex Trader’s Guide
SUMMARY OF ECONOMIC PROJECTIONS
There were meaningful changes in the September Summary of Economic Projections (SEP) compared to the material presented in June. In addition, the forecast horizon was extended to include estimates for 2025. The main details are highlighted below.
Source: Federal Reserve
FED DOT PLOT
The Fed’s so-called dot plot, which shows the trajectory for interest rates, signaled a more hawkish hiking path than contemplated a few months ago.
According to the updated diagram, officials expect to raise borrowing costs to 4.4% by December, implying about 120 basis points of additional tightening through year’s end. This reflects an upward revision of 100 bp from the material submitted in June. Participants then see the federal funds rate rising to 4.6% in 2023, 80 basis points higher than in the previous forecast. For 2024, the benchmark rate is expected to stand at 3.9%, compared to 3.4% before.
You May Like: Economic Activity – What is GDP Growth?
GPD AND UNEMPLOYEMENT
In June, the median projection for gross domestic product was 1.7% for this and next year, and 1.9% for 2024. The central bank downgraded these forecasts and now expects GDP to expand by 0.2%, 1.2% and 1.7%, respectively, over those three years, suggesting that the Fed is hell-bent on engineering a sustained period of below-trend growth to squash inflation.
Turning to unemployment, the new revisions were smaller, but still disappointing. At present, the labor market remains extremely tight, with demand for workers far outstripping labor supply, but this imbalance will begin to correct itself in the medium-term once the Fed's front-loaded actions fully play out in the real economy. In line with that logic, policymakers raised the jobless rate estimate for this year by one-tenth, to 3.8%. For 2023, the unemployment rate was marked up to 4.4% from 3.9% before.
Interesting Finding: The CPI and Forex - How CPI Data Affects Currency Prices
INFLATION
The median projection for core PCE, the central bank’s favorite inflation gauge, was boosted for 2022 and 2023 to 4.5% and 3.1% respectively. In the June’s Summary of Economic Projections, the outlook for this metric stood at 4.3%, 2.7% for these two periods.
Recommended by Diego Colman
Improve your trading with IG Client Sentiment Data
EDUCATION TOOLS FOR TRADERS
- Are you just getting started? Download the beginners’ guide for FX traders
- Would you like to know more about your trading personality? Take the DailyFX quiz and find out
- IG's client positioning data provides valuable information on market sentiment. Get your free guide on how to use this powerful trading indicator here.
---Written by Diego Colman, Market Strategist for DailyFX
Fed Hikes Rates by 75 bp to Curb Inflation. What’s Next for Gold, USD & Bitcoin? - DailyFX
Read More

No comments:
Post a Comment